


All about the eARTH
By MAISHA.A






The Crust of the Earth ............................7
layers of the Earth ..................7
Glossary...................................8



Introduction

Earth is a fascinating planet, full of life and wonders. Its diverse landscapes and unique position in the solar system makes it the perfect habitat for life. But how was it made?









Watch this video for more information!
The Big bang theory
Watch this video for more information!



15 billion years ago the whole universe was inside a tiny bubble called the cosmic egg, after some years it burst. They call that the big bang. When the planets cooled down, they started spinning causing wind and gravity. Due to all the pressure and gravity, a dead star was formed. The dead star started pulling giant dirty gas clouds, and it got denser and it formed an accretion disk. Over some time, other particles started sticking together creating larger objects until it was large enough to be called a planet. The Earth was hit by extremely hot asteroids, but when the Earth cooled down and formed a thin layer of crust, the water inside the Earth rose to the surface, making it look like the Earth we know today but a little bit different. But, we'll be learning a book about that later on.

Types of Tectonic Plates
The outermost layer of the earth is called the crust and it is broken into large pieces called tectonic plates. These huge pieces of Earth's surface slowly move at about the speed that your fingernails grow. Their movement form mountains and causes earthquakes and they even rearrange the position of continents.

Watch this for further information!
Here are how these plates change the Earth
As transformation plates rub against each other, huge stresses can cause portions of the rock to break, resulting in earthquakes. Places where these breaks occur are called faults.
Divergent plates cause earthquakes but also magma rises from the Earth's mantle to the surface, solidifying to create new oceanic crust.
Divergent plates causes earthquakes however Convergent don't.
As convergent plates collide towering mountain ranges, even sometimes it slips through and creates volcanoes.
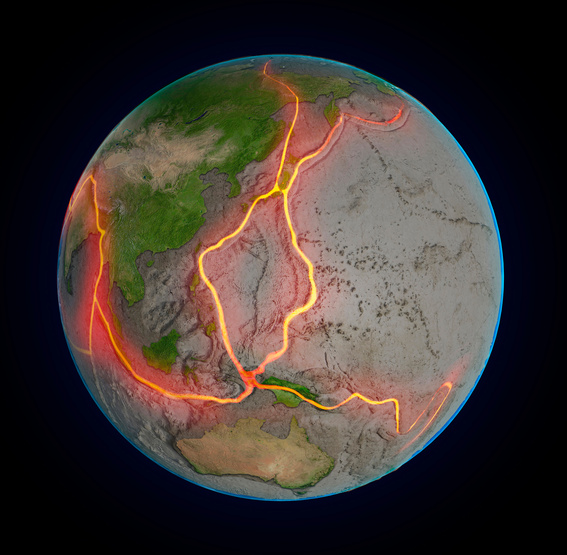


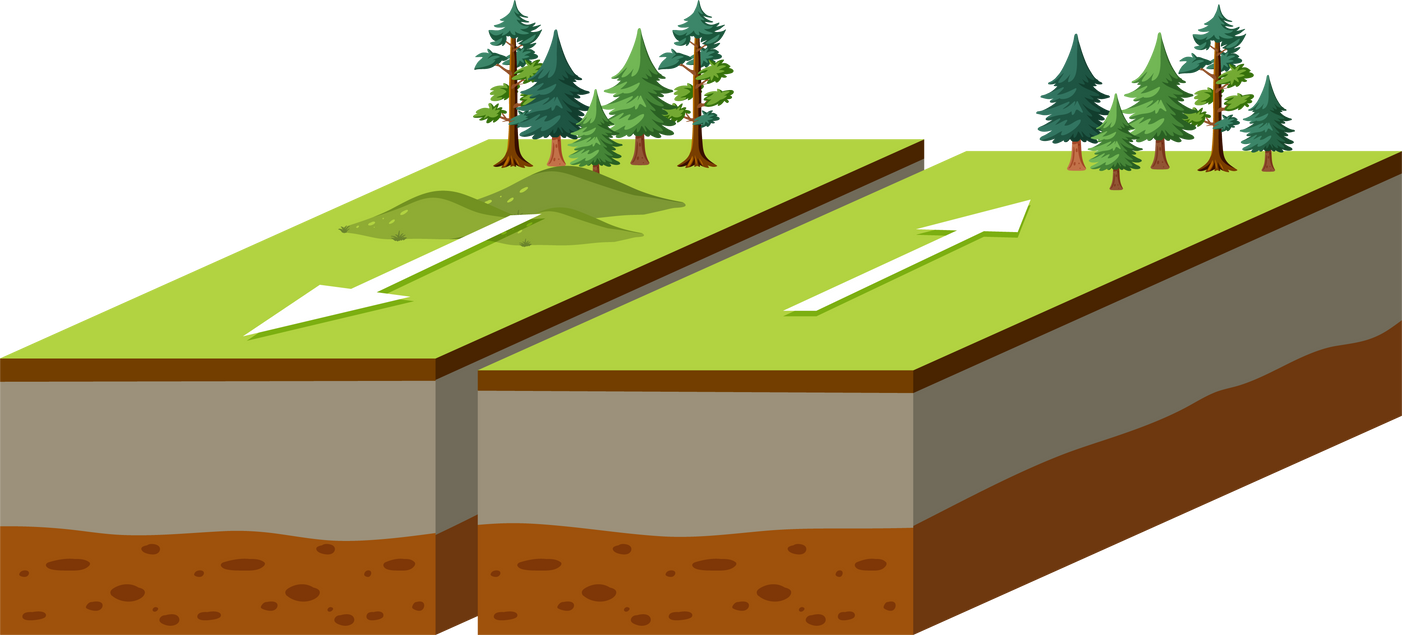
Transforming (sliding)
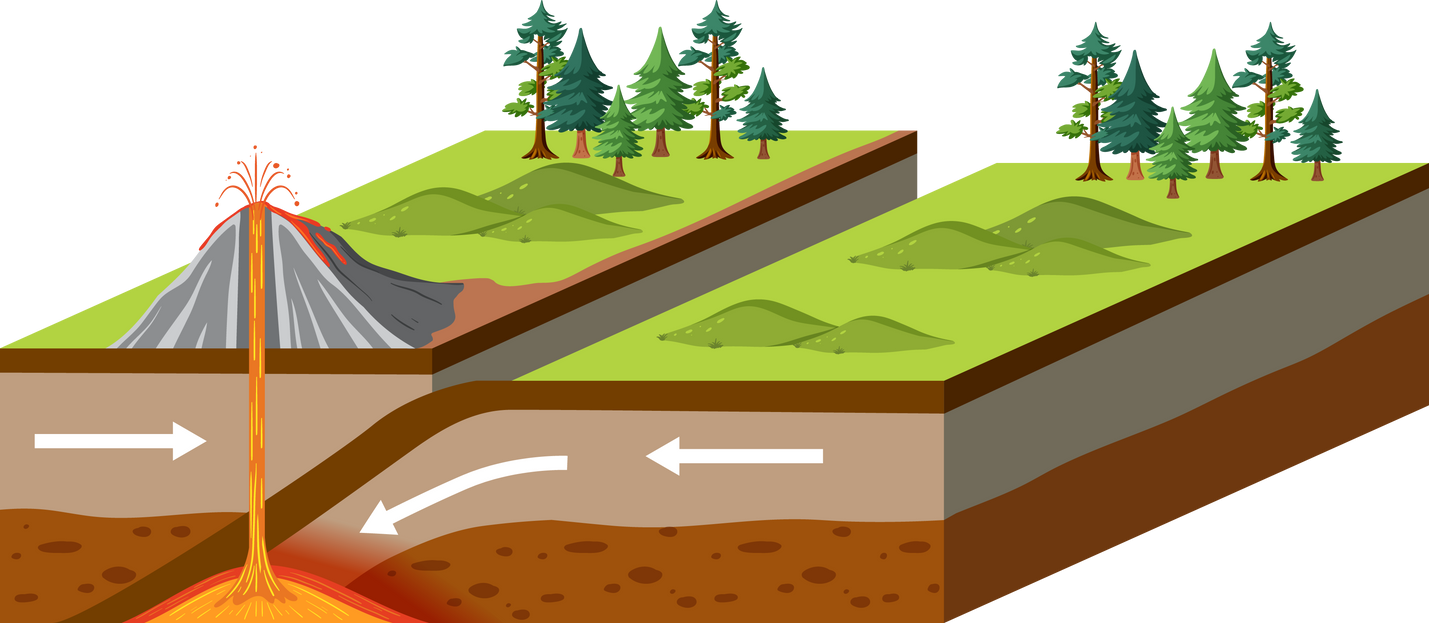
Convergent (colliding)
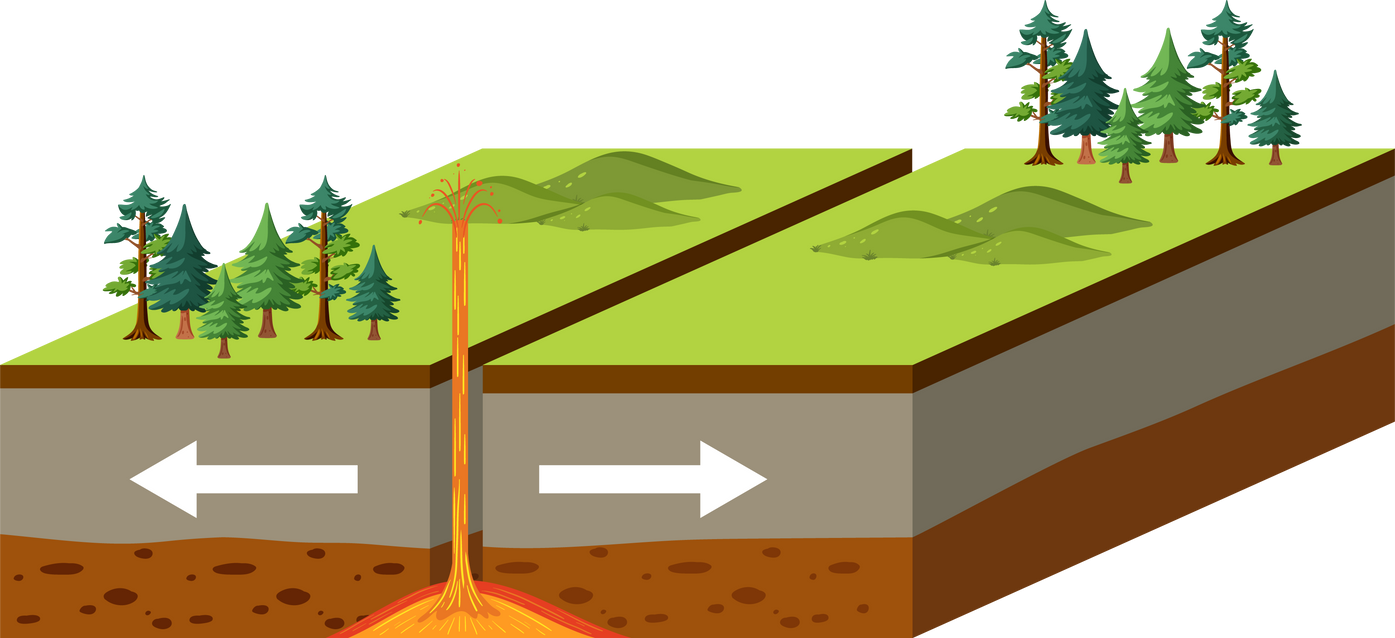
Divergen (pulling apart)
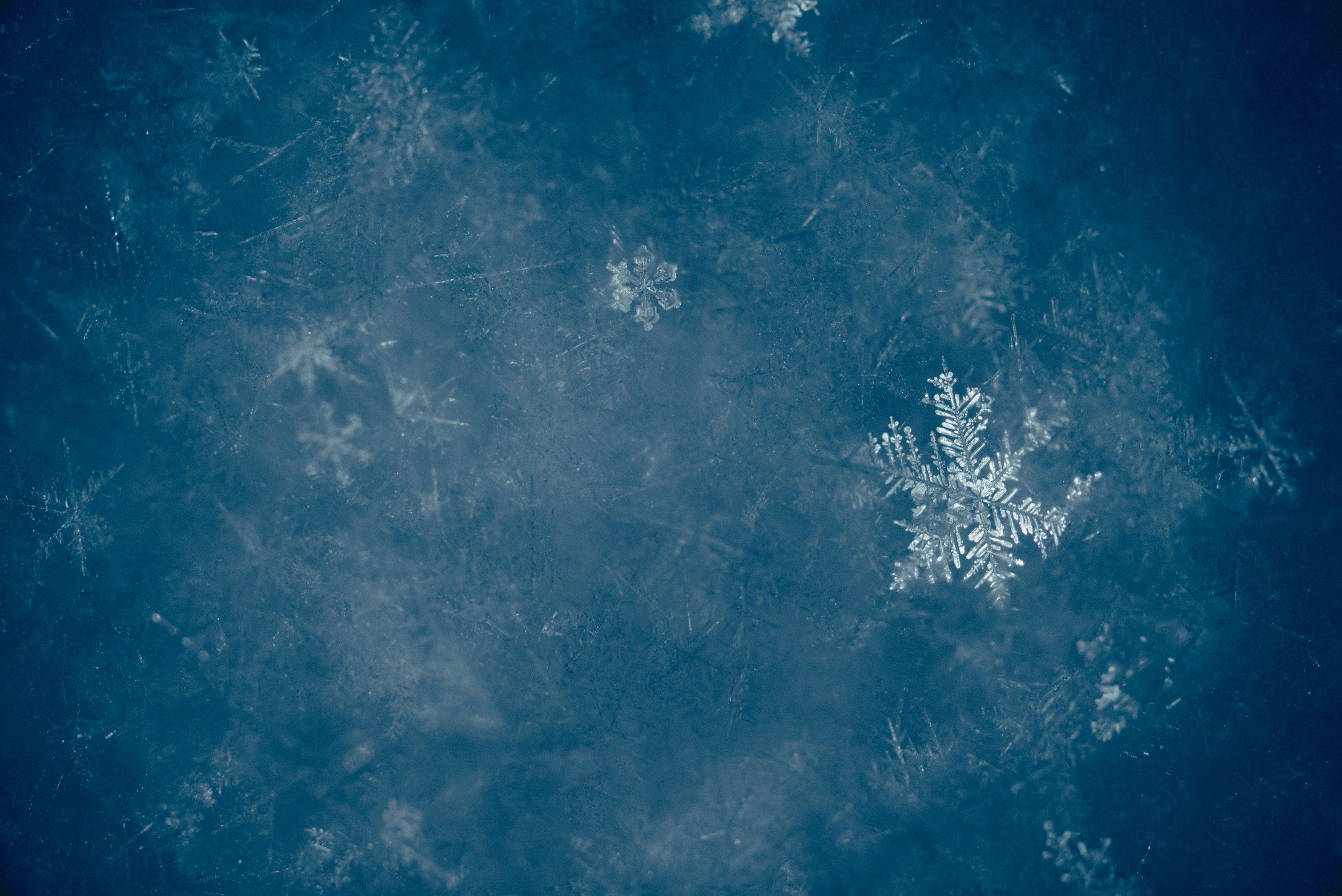



Our earth was covered in ice,there was no escape. Even if you were at the equator temperatures have would dipped below 0 degrees. Our earth used to look like this entirely covered with ice and snow. They called it the snowball Earth, and this icy mess happened two times. The Snowball Earth occurred between 460 to 430 million years ago. the snowball Earth refers to times when the Earth's surface was nearly or entirely Frozen. Scientists say these snowball earth events may have paved the way for the cambrian explosion of life that followed.


The MOON
Watch this video for more information!

The glowing thing in the night sky is called the Moon. Earth has just one moon – a rocky, cratered place, roughly a quarter the size of Earth and an average of 238,855 miles away. It's not a star or a planet, some people say it may have been running asteroids caught into the Earth's gravity making it the moon we know today. The moon rotates around the earth just like how the Earth rotates around the Sun. It takes about 27 days 4 hours and 43 minutes to go full circle but the moon can go over 1 mile every 2 seconds around the Earth. The Moon is a natural satellite. Its object that we did not create the orbits of the earth. You may notice that sometimes if you look at the Moon it might have a different color and this happens because our Earth's atmosphere.




Alfred Wegener

Alfred Wegener was born on November 1, 1880. This all started when he looked at a map and saw that Africa and South America look like it could fit together. He started asking people if continents were actually moving and it was a thing. He went to numerous places trying to find an answer. Eventually he found out the fossils from the same plant species were found on both sides across the Atlantic. once he gathered all his theories together he said that the continents used to be joined together and it was called Pangea. At first nobody believed him and nobody liked his theory. On November 13th 1930 Alfred Wegener was pronounced dead. Almost 50 years later Harry Hess confirmed Wegener's ideas by using the evidence of seafloor spreading to explain what moved continents.


Watch this video for more information!
Watch this video for more information!
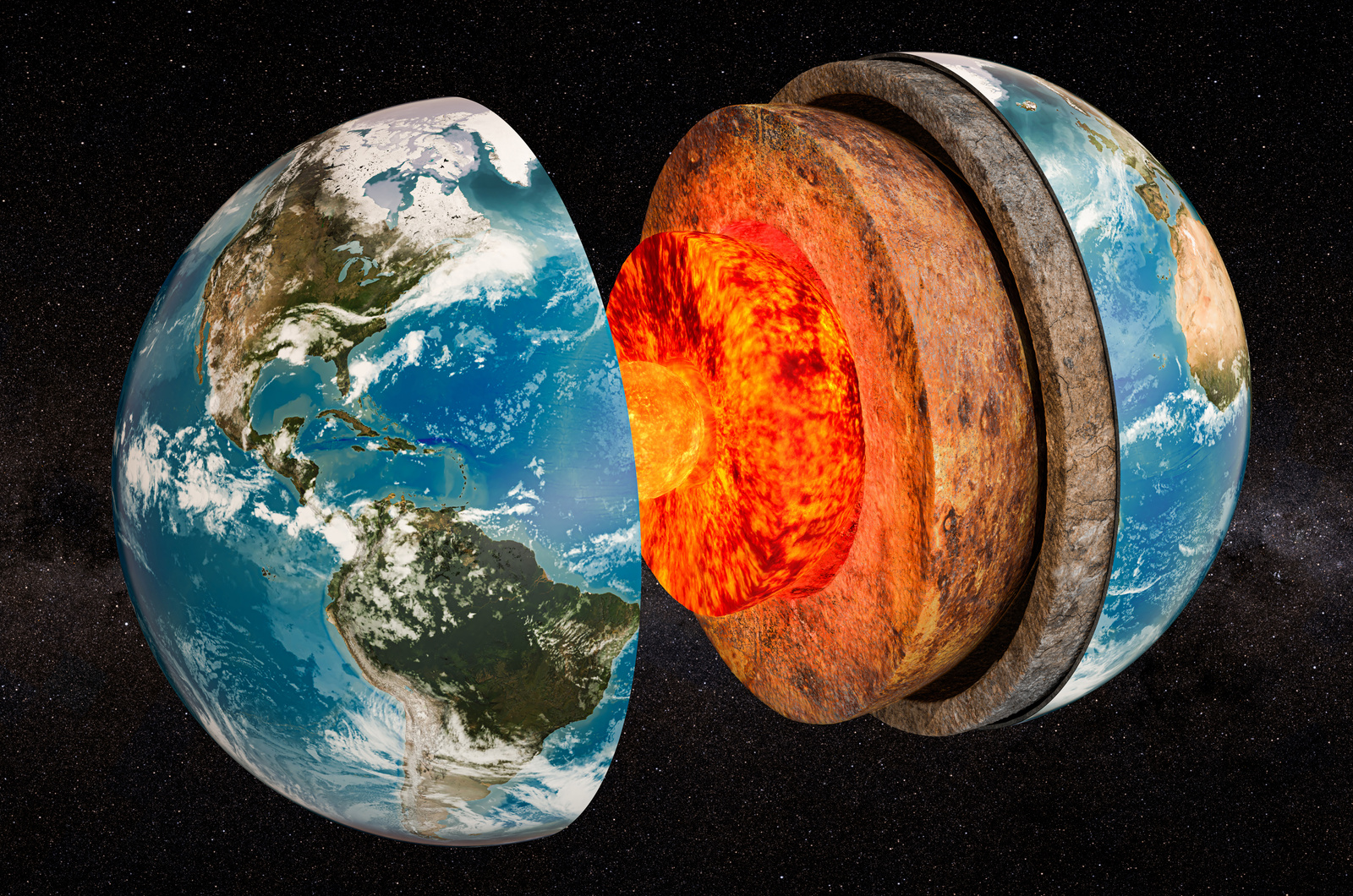
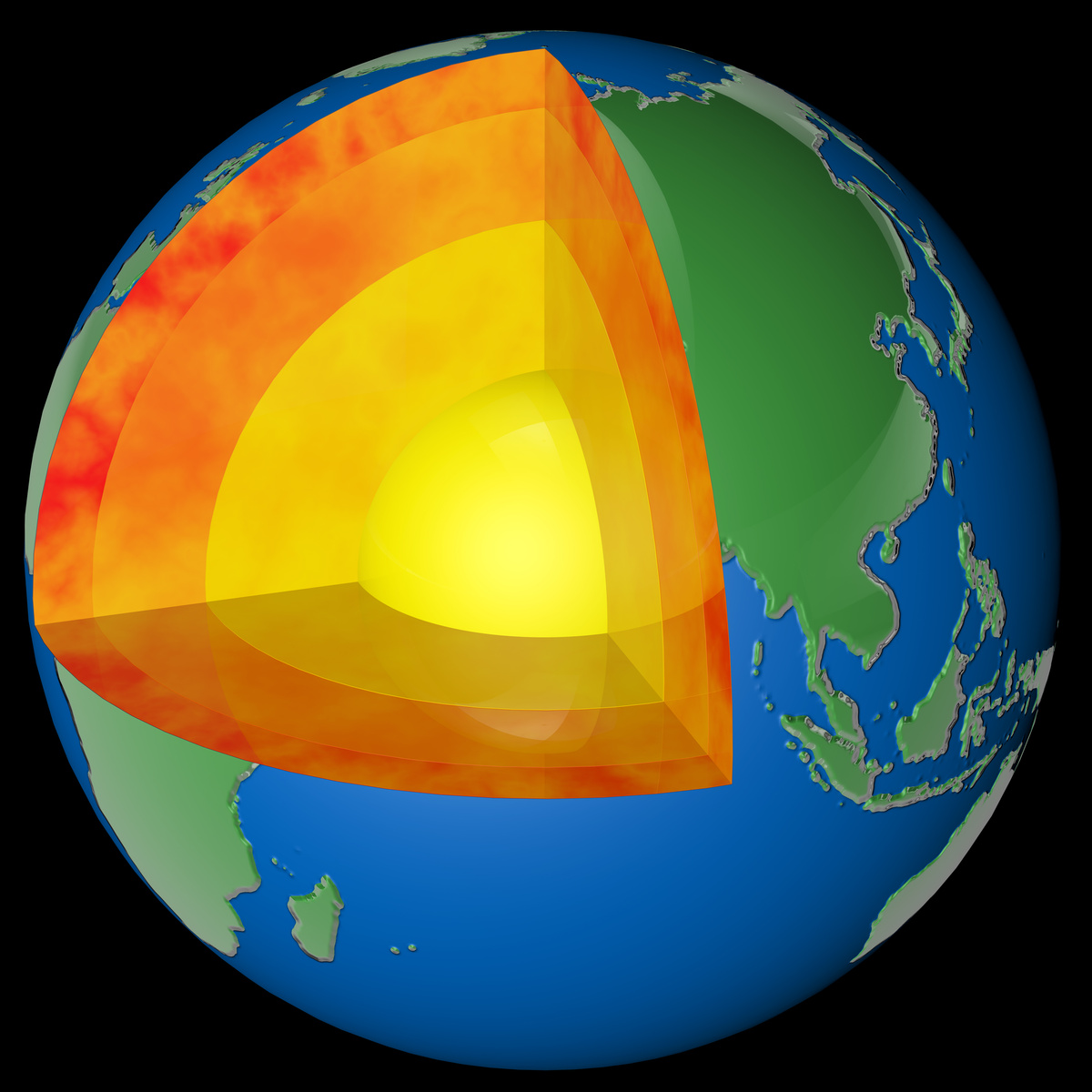
layers of the Earth
There are four main layers in the Earth, which is the crust, the mantle, the outer core, and the inner core. The crust is the thinnest layer of the Earth and it's also where we walk on our feet. The mantle is the hot gooey stuff that we call lava on the surface. The outer core is a liquid that surrounds the inner core it's mostly from iron and nickel. The inner core is a huge metal ball which is 2,500 km wide, and those are all the four main layers of the Earth.




Glossary

Asteroid: A rocky, irregularly shaped object that circles the sun. Asteroids range from a few feet to 600 miles (966 kilometers) across.

Continent: A single large continuous area of land
Crust: The layer of hard rocks that forms the surface of earth

Fault: A crack in Earth’s crust
Gravity: A pulling force that works across space
Lava: Melted rock that comes out of a volcano
Magma: Hot, liquid rock material within Earth
Mantle: The thick layer of rock under Earth’s crust
Volcano: A hold in Earth’s crust
Earthquake: A quaking, shaking, vibrating, or upheaval of Earth’s surface
Plate tectonics: The theory that Earth’s crust is made up of rigid plates that float on the asthenosphere
Satellite: A moon, planet or machine that orbits a planet or star


Fun facts
- The Big Bang Theory was first proposed by a catholic priest
- Albert Einstein didn’t believe the big bang theory at first
- The sun and moon aren't the same size




- Many of the major land continents appear to fit together like a jigsaw puzzle
- A majority of earthquake and volcanic activity occurs above plate boundaries
- During the snowball earth the earth's climate may have relied on methane to maintain surface temperatures above freezing

- There is water on the moon
- Alfred Wegener fought in World War l

- Alfred Wegener married his former mentor daughter
- The crust makes up only 1% of the volume of earth
- The most abundant elements in Earth's crust are oxygen and silicon
CREDITS
Books
Older than dirt, by Don Brown and Mike Perfit
Big Thanks To...

What are Natural Disasters, By Louise Spilsbury
Uncovering Earth's Crust, by Conrad J. Storad
Investigating Plate Tectonics by Greg Young
Earth by the numbers by Steve Jenkins